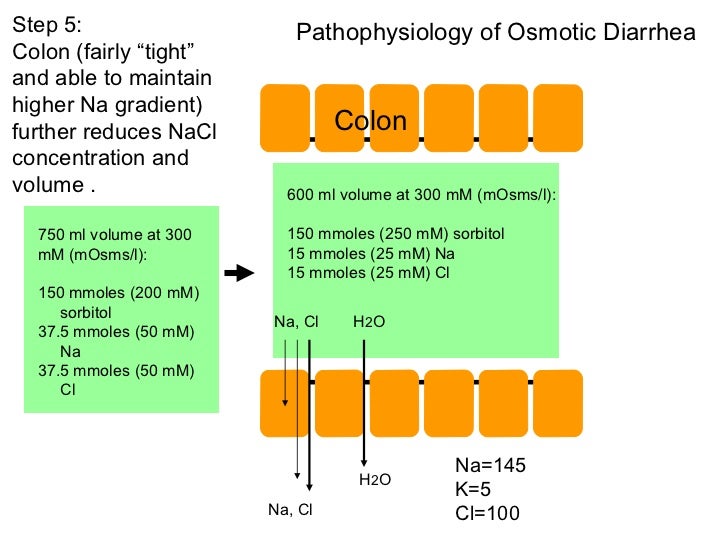
Diarrhea Stool Osmolality . the stool osmolar/osmotic gap determines if chronic diarrhea is osmotic or secretory in nature. osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in the intestine because of the presence of poorly absorbed solutes; this test measures the concentration (osmolality) of certain particles in a sample of your watery stool. Malabsorptive diarrhea is characterized by excess gas, steatorrhea, or weight loss;. Stool analysis revealing high stool osmotic gaps can help. the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory. in osmotic diarrhea, there is an unaccounted gap between the stool water electrolytes and the measured osmolality. in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool osmolality is almost entirely accounted for. in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. This gap is caused by poorly.
from www.slideshare.net
this test measures the concentration (osmolality) of certain particles in a sample of your watery stool. in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. the stool osmolar/osmotic gap determines if chronic diarrhea is osmotic or secretory in nature. Malabsorptive diarrhea is characterized by excess gas, steatorrhea, or weight loss;. This gap is caused by poorly. the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory. in osmotic diarrhea, there is an unaccounted gap between the stool water electrolytes and the measured osmolality. in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool osmolality is almost entirely accounted for. osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in the intestine because of the presence of poorly absorbed solutes; Stool analysis revealing high stool osmotic gaps can help.
01.26.12 Diarrhea and Malabsorption
Diarrhea Stool Osmolality the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory. This gap is caused by poorly. in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool osmolality is almost entirely accounted for. in osmotic diarrhea, there is an unaccounted gap between the stool water electrolytes and the measured osmolality. Stool analysis revealing high stool osmotic gaps can help. Malabsorptive diarrhea is characterized by excess gas, steatorrhea, or weight loss;. in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. the stool osmolar/osmotic gap determines if chronic diarrhea is osmotic or secretory in nature. osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in the intestine because of the presence of poorly absorbed solutes; the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory. this test measures the concentration (osmolality) of certain particles in a sample of your watery stool.
From www.slideshare.net
Gastroenterology Diarrhea Stool Osmolality the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory. osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in the intestine because of the presence of poorly absorbed solutes; the stool osmolar/osmotic gap determines if chronic diarrhea is osmotic or secretory in nature. This gap is caused by. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Acute Diarrhea & Gastroenteritis PowerPoint Presentation ID256314 Diarrhea Stool Osmolality in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in the intestine because of the presence of poorly absorbed solutes; in osmotic diarrhea, there is an unaccounted gap between the stool water electrolytes and the measured osmolality. Malabsorptive diarrhea is characterized by excess gas, steatorrhea, or weight. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT DIARRHEA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2120745 Diarrhea Stool Osmolality This gap is caused by poorly. Stool analysis revealing high stool osmotic gaps can help. in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool osmolality is almost entirely accounted for. Malabsorptive diarrhea is characterized by excess gas, steatorrhea, or weight loss;. the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory.. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From www.youtube.com
Secretory Diarrhea Vs Osmotic Diarrhea Explained YouTube Diarrhea Stool Osmolality Malabsorptive diarrhea is characterized by excess gas, steatorrhea, or weight loss;. in osmotic diarrhea, there is an unaccounted gap between the stool water electrolytes and the measured osmolality. in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool osmolality is almost entirely accounted for. Stool analysis revealing high stool osmotic gaps can help. in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From textarchive.ru
Chapter 2 Carcinoid Tumors Документ Diarrhea Stool Osmolality in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. This gap is caused by poorly. in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool osmolality is almost entirely accounted for. osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in the intestine because of the presence of poorly absorbed solutes; the next step when confronted with a chronic,. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From www.lecturio.com
Diarrhea Concise Medical Knowledge Diarrhea Stool Osmolality the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory. this test measures the concentration (osmolality) of certain particles in a sample of your watery stool. Stool analysis revealing high stool osmotic gaps can help. the stool osmolar/osmotic gap determines if chronic diarrhea is osmotic or secretory. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From www.slideshare.net
01.26.12 Diarrhea and Malabsorption Diarrhea Stool Osmolality this test measures the concentration (osmolality) of certain particles in a sample of your watery stool. osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in the intestine because of the presence of poorly absorbed solutes; in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool osmolality is almost entirely accounted for. in osmotic diarrhea, there is an unaccounted gap between the. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Diarrhea PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID249880 Diarrhea Stool Osmolality in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. This gap is caused by poorly. osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in the intestine because of the presence of poorly absorbed solutes; Malabsorptive diarrhea is characterized by excess gas, steatorrhea, or weight loss;. the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From exonkuxev.blob.core.windows.net
Define Stool Osmolality at Christine Poyner blog Diarrhea Stool Osmolality in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. Stool analysis revealing high stool osmotic gaps can help. This gap is caused by poorly. Malabsorptive diarrhea is characterized by excess gas, steatorrhea, or weight loss;. in osmotic diarrhea, there is an unaccounted gap between the stool water electrolytes and the measured osmolality. this test. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From slidetodoc.com
Approach To The Patient with Chronic Diarrhea Eric Diarrhea Stool Osmolality This gap is caused by poorly. the stool osmolar/osmotic gap determines if chronic diarrhea is osmotic or secretory in nature. Stool analysis revealing high stool osmotic gaps can help. the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory. osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT DIARRHEA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6311020 Diarrhea Stool Osmolality osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in the intestine because of the presence of poorly absorbed solutes; in osmotic diarrhea, there is an unaccounted gap between the stool water electrolytes and the measured osmolality. in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool osmolality is almost entirely accounted for. this test measures the concentration (osmolality) of certain particles. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From dxokrvgoz.blob.core.windows.net
Osmolality Stool Test at Samuel Mundy blog Diarrhea Stool Osmolality Malabsorptive diarrhea is characterized by excess gas, steatorrhea, or weight loss;. in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in the intestine because of the presence of poorly absorbed solutes; in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool osmolality is almost entirely accounted for. Stool analysis revealing high. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From slidetodoc.com
Gastrointestinal Block Pathology lecture 2013 Diarrhea Dr Maha Diarrhea Stool Osmolality in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. This gap is caused by poorly. osmotic diarrhea is caused by water retention in the intestine because of the presence of poorly absorbed solutes; Stool analysis revealing high stool osmotic gaps can help. in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool osmolality is almost entirely accounted for.. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From exonkuxev.blob.core.windows.net
Define Stool Osmolality at Christine Poyner blog Diarrhea Stool Osmolality the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory. Malabsorptive diarrhea is characterized by excess gas, steatorrhea, or weight loss;. the stool osmolar/osmotic gap determines if chronic diarrhea is osmotic or secretory in nature. This gap is caused by poorly. in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Malabsorption Group A PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Diarrhea Stool Osmolality in osmotic diarrhea, there is an unaccounted gap between the stool water electrolytes and the measured osmolality. in patients with secretory diarrhea, stool osmolality is almost entirely accounted for. This gap is caused by poorly. the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory. Malabsorptive diarrhea. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From probiotics.tips
💊 What Does Diarrhea Look Like? w/ chart Diarrhea Stool Osmolality This gap is caused by poorly. Malabsorptive diarrhea is characterized by excess gas, steatorrhea, or weight loss;. in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. in osmotic diarrhea, there is an unaccounted gap between the stool water electrolytes and the measured osmolality. this test measures the concentration (osmolality) of certain particles in a. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From cexbqgwy.blob.core.windows.net
Calculate Stool Osmolality at Shirly Metzger blog Diarrhea Stool Osmolality in osmotic diarrhea, there is an unaccounted gap between the stool water electrolytes and the measured osmolality. the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory. in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. the stool osmolar/osmotic gap determines if chronic. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.
From slideplayer.com
Gastrointestinal Block Pathology lecture ppt download Diarrhea Stool Osmolality This gap is caused by poorly. in osmotic diarrhea, the presence of uncharged solute or unmeasured cation in. the next step when confronted with a chronic, watery diarrhea is to determine whether it is an osmotic or secretory. the stool osmolar/osmotic gap determines if chronic diarrhea is osmotic or secretory in nature. Stool analysis revealing high stool. Diarrhea Stool Osmolality.